By
Unknown
Welcome to our OFFICIAL site.
Info & Outer plus info.SHARE.plus is the First and #1st info sharing service & helpful Globals Service in UNIVERSE/World~
.
Info & Outer plus info.SHARE.plus is the First and #1st info sharing service & helpful Globals Service in UNIVERSE/World~
.

Introduction :
The world's first information + sharing site ...
🔎ℹ . ♻ . ➕
@Info.Share.Plus
( DspPbtp)
Site Type: Internet Encyclopedia
Available: ####+ Version [1]
Owner: info.plus.Share.LTD [DspPbtp]
(Foundation)
Manufacturer: Md.TowfiqHossain, Sweet Dream,@Aah.Towfiq,(Dreamer) {Visionaries}[2]
Slogan :!!Always With You!! [Motto] "May Allah bless You"
Share the share + #info sharing encyclopedia, that anyone can edit info.plus sharing.
Chants : Just For You info.SHARE.plus.
The world's #1st information + sharing site ...
Founder: All-Arafat Hasan Towfiq, Al-Arafat Hasan Fahim
Chief person: Md.TowfiqHossain (CAO)
Website: http://m.me/info.share.plus
Alexa location:
Unchanged 5 (global, December, 2010+)
"Commercial"
Registration: Optional [notes 1]
Users: 18686+ active editors [note 1] and 1,86,486+ registered editors;
Start date: January 4, 1999; +
Current conditions: Active;
Content License: Info.Share / Share-Alike 3.0
With the small contribution of everyone to the SIP web culture, this site has become an increasingly organized collection. Currently it will be used as the largest and most popular Internet based references.
Info.Shar.Plus is an information exchange website. One of the key drivers of Web 3.0+ is info.share.plus will be a very popular InfoPlus sharing site in the current Internet world, which will provide its users with information + upload, sharing, sharing and sharing. This site will also have more info.plus reviews, opinions and other useful features.
In 2018, Active.info.Plus acknowledges that, along with @ Info.Share.plus (YouTube, Reddit, MySpace, and Facebook) [15], online collaboration and interaction with millions of people worldwide will grow rapidly. It will also gain reputation as a news source due to the rapid updates regarding the immediate news of the Info.Share.Plus article.
Since the Info.Share.plus website is open-ended, various initiatives have been undertaken to protect the value of writing, [19] vandalism and accuracy of information.
"Info.Share.Plus" (Information Sharing & INFO.SHARE.PLUS)
#The_Earth's_first_informtion_sharing_service & helpful services.
Important information is displayed on Info.Share.plus;
* + Would be very happy if you read them and tell Info.Share.plus your comments and cooperate well.
E-mail: info.share.plus.towfiq@gmail.com
"Info.Share.Plus"
ℹ. ♻. ➕
🔎🆔Info.Share.Plus
💻 (ℹ♻➕) 🌎
More ...
"DPBT.plus" Group:
COMPUTER
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia "Computer system" redirects here. For other uses, see Computer (disambiguation) and Computer system (disambiguation).|
Computers and computing devices from different eras
|
A computer is a device that can be instructed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations automatically via computer programming. Modern computers have the ability to follow generalized sets of operations, called programs.These programs enable computers to perform an extremely wide range of tasks.
Computers are used as control systems for a wide variety of industrial and consumer devices. This includes simple special purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, factory devices such as industrial robots and computer-aided design, and also general purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones.
Early computers were only conceived as calculating devices. Since ancient times, simple manual devices like the abacus aided people in doing calculations. Early in the Industrial Revolution, some mechanical devices were built to automate long tedious tasks, such as guiding patterns for looms. More sophisticated electrical machines did specialized analog calculations in the early 20th century. The first digital electronic calculating machines were developed during World War II. The speed, power, and versatility of computers have been increasing dramatically ever since then.
Conventionally, a modern computer consists of at least one processing element, typically a central processing unit (CPU), and some form of memory. The processing element carries out arithmetic and logical operations, and a sequencing and control unit can change the order of operations in response to stored information. Peripheral devices include input devices (keyboards, mice, joystick, etc.), output devices (monitor screens, printers, etc.), and input/output devices that perform both functions (e.g., the 2000s-era touchscreen). Peripheral devices allow information to be retrieved from an external source and they enable the result of operations to be saved and retrieved.
Web Design and Development
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Lorem ipsum dolor sit AIP,Web design
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Web design encompasses many different skills and disciplines in the production and maintenance of websites. The different areas of web design include web graphic design; interface design; authoring, including standardised code and proprietary software; user experience design; and search engine optimization. Often many individuals will work in teams covering different aspects of the design process, although some designers will cover them all.[1] The term web design is normally used to describe the design process relating to the front-end (client side) design of a website including writing mark up. Web design partially overlaps web engineering in the broader scope of web development. Web designers are expected to have an awareness of usability and if their role involves creating mark up then they are also expected to be up to date with web accessibility guidelines.
Contents
History
1988–2001
Although web design has a fairly recent history, it can be linked to other areas such as graphic design. However, web design can also be seen from a technological standpoint. It has become a large part of people’s everyday lives. It is hard to imagine the Internet without animated graphics, different styles of typography, background, and music.
The start of the web and web design
In 1989, whilst working at CERN Tim Berners-Lee proposed to create a global hypertext project, which later became known as the World Wide Web. During 1991 to 1993 the World Wide Web was born. Text-only pages could be viewed using a simple line-mode browser.[2] In 1993 Marc Andreessen and Eric Bina, created the Mosaic browser. At the time there were multiple browsers, however the majority of them were Unix-based and naturally text heavy. There had been no integrated approach to graphic design elements such as images or sounds. The Mosaic browser broke this mould.[3] The W3C was created in October 1994 to "lead the World Wide Web to its full potential by developing common protocols that promote its evolution and ensure its interoperability."[4] This discouraged any one company from monopolizing a propriety browser and programming language, which could have altered the effect of the World Wide Web as a whole. The W3C continues to set standards, which can today be seen with JavaScript. In 1994 Andreessen formed Communications Corp. that later became known as Netscape Communications, the Netscape 0.9 browser. Netscape created its own HTML tags without regard to the traditional standards process. For example, Netscape 1.1 included tags for changing background colours and formatting text with tables on web pages. Throughout 1996 to 1999 the browser wars began, as Microsoft and Netscape fought for ultimate browser dominance. During this time there were many new technologies in the field, notably Cascading Style Sheets, JavaScript, and Dynamic HTML. On the whole, the browser competition did lead to many positive creations and helped web design evolve at a rapid pace.[5]
Evolution of web design
In 1996, Microsoft released its first competitive browser, which was complete with its own features and tags. It was also the first browser to support style sheets, which at the time was seen as an obscure authoring technique.[5] The HTML markup for tables was originally intended for displaying tabular data. However designers quickly realized the potential of using HTML tables for creating the complex, multi-column layouts that were otherwise not possible. At this time, as design and good aesthetics seemed to take precedence over good mark-up structure, and little attention was paid to semantics and web accessibility. HTML sites were limited in their design options, even more so with earlier versions of HTML. To create complex designs, many web designers had to use complicated table structures or even use blank spacer .GIF images to stop empty table cells from collapsing.[6] CSS was introduced in December 1996 by the W3C to support presentation and layout. This allowed HTML code to be semantic rather than both semantic and presentational, and improved web accessibility, see tableless web design.
In 1996, Flash (originally known as FutureSplash) was developed. At the time, the Flash content development tool was relatively simple compared to now, using basic layout and drawing tools, a limited precursor to ActionScript, and a timeline, but it enabled web designers to go beyond the point of HTML, animated GIFs and JavaScript. However, because Flash required a plug-in, many web developers avoided using it for fear of limiting their market share due to lack of compatibility. Instead, designers reverted to gif animations (if they didn't forego using motion graphics altogether) and JavaScript for widgets. But the benefits of Flash made it popular enough among specific target markets to eventually work its way to the vast majority of browsers, and powerful enough to be used to develop entire sites.[6]
End of the first browser wars
During 1998 Netscape released Netscape Communicator code under an open source licence, enabling thousands of developers to participate in improving the software. However, they decided to start from the beginning, which guided the development of the open source browser and soon expanded to a complete application platform.[5] The Web Standards Project was formed and promoted browser compliance with HTML and CSS standards by creating Acid1, Acid2, and Acid3 tests. 2000 was a big year for Microsoft. Internet Explorer was released for Mac; this was significant as it was the first browser that fully supported HTML 4.01 and CSS 1, raising the bar in terms of standards compliance. It was also the first browser to fully support the PNG image format.[5] During this time Netscape was sold to AOL and this was seen as Netscape’s official loss to Microsoft in the browser wars.[5]
2001–2012
Since the start of the 21st century the web has become more and more integrated into peoples lives. As this has happened the technology of the web has also moved on. There have also been significant changes in the way people use and access the web, and this has changed how sites are designed.
Since the end of the browsers wars[when?] new browsers have been released. Many of these are open source meaning that they tend to have faster development and are more supportive of new standards. The new options are considered by many[weasel words] to be better than Microsoft's Internet Explorer.
The W3C has released new standards for HTML (HTML5) and CSS (CSS3), as well as new JavaScript API's, each as a new but individual standard.[when?] While the term HTML5 is only used to refer to the new version of HTML and some of the JavaScript API's, it has become common to use it to refer to the entire suite of new standards (HTML5, CSS3 and JavaScript).
Tools and technologies
Web designers use a variety of different tools depending on what part of the production process they are involved in. These tools are updated over time by newer standards and software but the principles behind them remain the same. Web designers use both vector and raster graphics editors to create web-formatted imagery or design prototypes. Technologies used to create websites include W3C standards like HTML and CSS, which can be hand-coded or generated by WYSIWYG editing software. Other tools web designers might use include mark up validators[7] and other testing tools for usability and accessibility to ensure their websites meet web accessibility guidelines.[8]
Skills and techniques
Marketing and communication design
Marketing and communication design on a website may identify what works for its target market. This can be an age group or particular strand of culture; thus the designer may understand the trends of its audience. Designers may also understand the type of website they are designing, meaning, for example, that (B2B) business-to-business website design considerations might differ greatly from a consumer targeted website such as a retail or entertainment website. Careful consideration might be made to ensure that the aesthetics or overall design of a site do not clash with the clarity and accuracy of the content or the ease of web navigation,[9] especially on a B2B website. Designers may also consider the reputation of the owner or business the site is representing to make sure they are portrayed favourably.
User experience design and interactive design
User understanding of the content of a website often depends on user understanding of how the website works. This is part of the user experience design. User experience is related to layout, clear instructions and labeling on a website. How well a user understands how they can interact on a site may also depend on the interactive design of the site. If a user perceives the usefulness of the website, they are more likely to continue using it. Users who are skilled and well versed with website use may find a more distinctive, yet less intuitive or less user-friendly website interface useful nonetheless. However, users with less experience are less likely to see the advantages or usefulness of a less intuitive website interface. This drives the trend for a more universal user experience and ease of access to accommodate as many users as possible regardless of user skill.[10] Much of the user experience design and interactive design are considered in the user interface design.
Advanced interactive functions may require plug-ins if not advanced coding language skills. Choosing whether or not to use interactivity that requires plug-ins is a critical decision in user experience design. If the plug-in doesn't come pre-installed with most browsers, there's a risk that the user will have neither the know how or the patience to install a plug-in just to access the content. If the function requires advanced coding language skills, it may be too costly in either time or money to code compared to the amount of enhancement the function will add to the user experience. There's also a risk that advanced interactivity may be incompatible with older browsers or hardware configurations. Publishing a function that doesn't work reliably is potentially worse for the user experience than making no attempt. It depends on the target audience if it's likely to be needed or worth any risks.
Page layout
Part of the user interface design is affected by the quality of the page layout. For example, a designer may consider whether the site's page layout should remain consistent on different pages when designing the layout. Page pixel width may also be considered vital for aligning objects in the layout design. The most popular fixed-width websites generally have the same set width to match the current most popular browser window, at the current most popular screen resolution, on the current most popular monitor size. Most pages are also center-aligned for concerns of aesthetics on larger screens.
Fluid layouts increased in popularity around 2000 as an alternative to HTML-table-based layouts and grid-based design in both page layout design principle and in coding technique, but were very slow to be adopted.[note 1] This was due to considerations of screen reading devices and varying windows sizes which designers have no control over. Accordingly, a design may be broken down into units (sidebars, content blocks, embedded advertising areas, navigation areas) that are sent to the browser and which will be fitted into the display window by the browser, as best it can. As the browser does recognize the details of the reader's screen (window size, font size relative to window etc.) the browser can make user-specific layout adjustments to fluid layouts, but not fixed-width layouts. Although such a display may often change the relative position of major content units, sidebars may be displaced below body text rather than to the side of it. This is a more flexible display than a hard-coded grid-based layout that doesn't fit the device window. In particular, the relative position of content blocks may change while leaving the content within the block unaffected. This also minimizes the user's need to horizontally scroll the page.
Responsive Web Design is a newer approach, based on CSS3, and a deeper level of per-device specification within the page's stylesheet through an enhanced use of the CSS
@media rule. In March 2018 Google announced they would be rolling out mobile-first indexing.[11]Sites using responsive design are well placed to ensure they meet this new approach.Typography
Web designers may choose to limit the variety of website typefaces to only a few which are of a similar style, instead of using a wide range of typefaces or type styles. Most browsers recognize a specific number of safe fonts, which designers mainly use in order to avoid complications.
Font downloading was later included in the CSS3 fonts module and has since been implemented in Safari 3.1, Opera 10 and Mozilla Firefox 3.5. This has subsequently increased interest in web typography, as well as the usage of font downloading.
Most site layouts incorporate negative space to break the text up into paragraphs and also avoid center-aligned text.[12]
Motion graphics
The page layout and user interface may also be affected by the use of motion graphics. The choice of whether or not to use motion graphics may depend on the target market for the website. Motion graphics may be expected or at least better received with an entertainment-oriented website. However, a website target audience with a more serious or formal interest (such as business, community, or government) might find animations unnecessary and distracting if only for entertainment or decoration purposes. This doesn't mean that more serious content couldn't be enhanced with animated or video presentations that is relevant to the content. In either case, motion graphic design may make the difference between more effective visuals or distracting visuals.
Motion graphics that are not initiated by the site visitor can produce accessibility issues. The World Wide Web consortium accessibility standards require that site visitors be able to disable the animations.[13]
Quality of code
Website designers may consider it to be good practice to conform to standards. This is usually done via a description specifying what the element is doing. Failure to conform to standards may not make a website unusable or error prone, but standards can relate to the correct layout of pages for readability as well making sure coded elements are closed appropriately. This includes errors in code, more organized layout for code, and making sure IDs and classes are identified properly. Poorly-coded pages are sometimes colloquially called tag soup. Validating via W3C[7] can only be done when a correct DOCTYPE declaration is made, which is used to highlight errors in code. The system identifies the errors and areas that do not conform to web design standards. This information can then be corrected by the user.[14]
Generated content
There are two ways websites are generated: statically or dynamically.
Static websites
Main article: Static web page
A static website stores a unique file for every page of a static website. Each time that page is requested, the same content is returned. This content is created once, during the design of the website. It is usually manually authored, although some sites use an automated creation process, similar to a dynamic website, whose results are stored long-term as completed pages. These automatically-created static sites became more popular around 2015, with generators such as Jekyll and Adobe Muse.[15]
The benefits of a static website are that they were simpler to host, as their server only needed to serve static content, not execute server-side scripts. This required less server administration and had less chance of exposing security holes. They could also serve pages more quickly, on low-cost server hardware. These advantage became less important as cheap web hosting expanded to also offer dynamic features, and virtual servers offered high performance for short intervals at low cost.
Almost all websites have some static content, as supporting assets such as images and stylesheets are usually static, even on a website with highly dynamic pages.
Dynamic websites
Main article: Dynamic web page
Dynamic websites are generated on the fly and use server-side technology to generate webpages. They typically extract their content from one or more back-end databases: some are database queries across a relational database to query a catalogue or to summarise numeric information, others may use a document database such as MongoDB or NoSQL to store larger units of content, such as blog posts or wiki articles.
In the design process, dynamic pages are often mocked-up or wireframed using static pages. The skillset needed to develop dynamic web pages is much broader than for a static pages, involving server-side and database coding as well as client-side interface design. Even medium-sized dynamic projects are thus almost always a team effort.
When dynamic web pages first developed, they were typically coded directly in languages such as Perl, PHP or ASP. Some of these, notably PHP and ASP, used a 'template' approach where a server-side page resembled the structure of the completed client-side page and data was inserted into places defined by 'tags'. This was a quicker means of development than coding in a purely procedural coding language such as Perl.
Both of these approaches have now been supplanted for many websites by higher-level application-focused tools such as content management systems. These build on top of general purpose coding platforms and assume that a website exists to offer content according to one of several well recognised models, such as a time-sequenced blog, a thematic magazine or news site, a wiki or a user forum. These tools make the implementation of such a site very easy, and a purely organisational and design-based task, without requiring any coding.
Editing the content itself (as well as the template page) can be done both by means of the site itself, and with the use of third-party software. The ability to edit all pages is provided only to a specific category of users (for example, administrators, or registered users). In some cases, anonymous users are allowed to edit certain web content, which is less frequent (for example, on forums - adding messages). An example of a site with an anonymous change is Wikipedia.
Homepage design
Usability experts, including Jakob Nielsen and Kyle Soucy, have often emphasised homepage design for website success and asserted that the homepage is the most important page on a website.[16][17][18][19] However practitioners into the 2000s were starting to find that a growing number of website traffic was bypassing the homepage, going directly to internal content pages through search engines, e-newsletters and RSS feeds.[20] Leading many practitioners to argue that homepages are less important than most people think.[21][22][23][24] Jared Spool argued in 2007 that a site's homepage was actually the least important page on a website.[25]
In 2012 and 2013, carousels (also called 'sliders' and 'rotating banners') have become an extremely popular design element on homepages, often used to showcase featured or recent content in a confined space.[26][27] Many practitioners argue that carousels are an ineffective design element and hurt a website's search engine optimisation and usability.[27][28][29]
Occupations
There are two primary jobs involved in creating a website: the web designer and web developer, who often work closely together on a website.[30] The web designers are responsible for the visual aspect, which includes the layout, coloring and typography of a web page. Web designers will also have a working knowledge of markup languages such as HTML and CSS, although the extent of their knowledge will differ from one web designer to another. Particularly in smaller organizations one person will need the necessary skills for designing and programming the full web page, while larger organizations may have a web designer responsible for the visual aspect alone.[31]
Further jobs which may become involved in the creation of a website include:
- Graphic designers to create visuals for the site such as logos, layouts and buttons
- Internet marketing specialists to help maintain web presence through strategic solutions on targeting viewers to the site, by using marketing and promotional techniques on the internet
- SEO writers to research and recommend the correct words to be incorporated into a particular website and make the website more accessible and found on numerous search engines
- Internet copywriter to create the written content of the page to appeal to the targeted viewers of the site[1]
- User experience (UX) designer incorporates aspects of user focused design considerations which include information architecture, user centered design, user testing, interaction design, and occasionally visual design.
See also
See also
Related disciplines
Notes
- Jump up^
<table>-based markup and spacer .GIF images
- ^ Jump up to:a b Lester, Georgina. "Different jobs and responsibilities of various people involved in creating a website". Arts Wales UK. Retrieved 2012-03-17.
- Jump up^ "Longer Biography". Retrieved 2012-03-16.
- Jump up^ "Mosaic Browser" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-03-16.
- Jump up^ Zwicky, E.D, Cooper, S and Chapman, D.B. (2000). Building Internet Firewalls. United States: O’Reily & Associates. p. 804. ISBN 1-56592-871-7.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Niederst, Jennifer (2006). Web Design In a Nutshell. United States of America: O'Reilly Media. pp. 12–14. ISBN 0-596-00987-9.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Chapman, Cameron, The Evolution of Web Design, Six Revisions, archived from the original on 30 October 2013
- ^ Jump up to:a b "W3C Markup Validation Service".
- Jump up^ W3C. "Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI)".
- Jump up^ THORLACIUS, LISBETH (2007). "The Role of Aesthetics in Web Design". Nordicom Review (28): 63–76. Retrieved 2014-07-18.
- Jump up^ Castañeda, J.A Francisco; Muñoz-Leiva, Teodoro Luque (2007). "Web Acceptance Model (WAM): Moderating effects of user experience". Information & Management. 44: 384–396. doi:10.1016/j.im.2007.02.003.
- Jump up^ "Rolling out mobile-first indexing". Official Google Webmaster Central Blog. Retrieved 2018-06-09.
- Jump up^ Stone, John (2009-11-16). "20 Do's and Don'ts of Effective Web Typography". Retrieved 2012-03-19.
- Jump up^ World Wide Web Consortium: Understanding Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.2.2: Pause, Stop, Hide
- Jump up^ W3C QA. "My Web site is standard! And yours?". Retrieved 2012-03-21.
- Jump up^ Christensen, Mathias Biilmann (2015-11-16). "Static Website Generators Reviewed: Jekyll, Middleman, Roots, Hugo". Smashing Magazine. Retrieved 2016-10-26.
- Jump up^ Soucy, Kyle, Is Your Homepage Doing What It Should?, Usable Interface, archived from the original on 8 June 2012
- Jump up^ Nielsen & Tahir 2001.
- Jump up^ Nielsen, Jakob (10 November 2003), The Ten Most Violated Homepage Design Guidelines, Nielsen Norman Group, archived from the original on 5 October 2013
- Jump up^ Knight, Kayla (20 August 2009), Essential Tips for Designing an Effective Homepage, Six Revisions, archived from the original on 21 August 2013
- Jump up^ Spool, Jared (29 September 2005), Is Home Page Design Relevant Anymore?, User Interface Engineering, archived from the original on 16 September 2013
- Jump up^ Chapman, Cameron (15 September 2010), 10 Usability Tips Based on Research Studies, Six Revisions, archived from the original on 2 September 2013
- Jump up^ Gócza, Zoltán, Myth #17: The homepage is your most important page, archived from the original on 2 June 2013
- Jump up^ McGovern, Gerry (18 April 2010), The decline of the homepage, archived from the original on 24 May 2013
- Jump up^ Porter, Joshua (24 April 2006), Prioritizing Design Time: A Long Tail Approach, User Interface Engineering, archived from the original on 14 May 2013
- Jump up^ Spool, Jared (6 August 2007), Usability Tools Podcast: Home Page Design, archived from the original on 29 April 2013
- Jump up^ Bates, Chris (9 October 2012), Best practices in carousel design for effective web marketing, Smart Insights, archived from the original on 3 April 2013
- ^ Jump up to:a b Messner, Katie (22 April 2013), Image Carousels: Getting Control of the Merry-Go-Round, Usability.gov, archived from the original on 10 October 2013
- Jump up^ Jones, Harrison (19 June 2013), Homepage Sliders: Bad For SEO, Bad For Usability, archived from the original on 22 November 2013
- Jump up^ Laja, Peep (27 September 2012), Don’t Use Automatic Image Sliders or Carousels, Ignore the Fad, ConversionXL, archived from the original on 25 November 2013
- Jump up^ Oleksy, Walter (2001). Careers in Web Design. New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, Inc. pp. 9–11. ISBN 9780823931910.
- Jump up^ "Web Designer". Retrieved 2012-03-19.
References and further reading
- Nielsen, Jakob; Tahir, Marie (October 2001), Homepage Usability: 50 Websites Deconstructed, New Riders Publishing, ISBN 978-0735711020
External links
- W3C consortium for web standards
- Web design and development at Curlie (based on DMOZ)
| Portals Access related topics | |
| Find out more on Wikipedia's Sister projects |
|
Navigation menu
- This page was last edited on 29 June 2018, at 12:24 (UTC).
- Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
- Privacy policy
- About Wikipedia
- Disclaimers
- Contact Wikipedia
- Developers
- Cookie statement
- Mobile view
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the company. For the search engine, see Google Search. For other uses, see Google (disambiguation).
Not to be confused with Googol.

Google's logo since 2015
| |

Google's headquarters, the Googleplex, in August 2014
| |
Formerly
| Google Inc. (1998–2017) |
|---|---|
| Subsidiary | |
| Industry |
|
| Founded | September 4, 1998 (20 years ago) in Menlo Park, California[1][2] |
| Founders | |
| Headquarters | 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, California, U.S.[3] |
Area served
| Worldwide |
Key people
| |
| Products | List of Google products |
Number of employees
| 85,050[4] (Q1 2018) |
| Parent | Alphabet Inc. (2015–present) |
| Subsidiaries | List of subsidiaries |
| Website | google |
Google LLC[5] is an American multinational technology company that specializes in Internet-related services and products, which include online advertising technologies, search engine, cloud computing, software, and hardware. Google was founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin while they were Ph.D. students at Stanford University in California. Together they own about 14 percent of its shares and control 56 percent of the stockholder voting power through supervoting stock. They incorporated Google as a privately held company on September 4, 1998. An initial public offering (IPO) took place on August 19, 2004, and Google moved to its headquarters in Mountain View, California, nicknamed the Googleplex. In August 2015, Google announced plans to reorganize its various interests as a conglomerate called Alphabet Inc. Google is Alphabet's leading subsidiary and will continue to be the umbrella company for Alphabet's Internet interests. Sundar Pichai was appointed CEO of Google, replacing Larry Page who became the CEO of Alphabet.
The company's rapid growth since incorporation has triggered a chain of products, acquisitions, and partnerships beyond Google's core search engine (Google Search). It offers services designed for work and productivity (Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides), email (Gmail/Inbox), scheduling and time management (Google Calendar), cloud storage (Google Drive), social networking (Google+), instant messaging and video chat (Google Allo, Duo, Hangouts), language translation (Google Translate), mapping and navigation (Google Maps, Waze, Google Earth, Street View), video sharing (YouTube), note-taking (Google Keep), and photo organizing and editing (Google Photos). The company leads the development of the Android mobile operating system, the Google Chrome web browser, and Chrome OS, a lightweight operating system based on the Chrome browser. Google has moved increasingly into hardware; from 2010 to 2015, it partnered with major electronics manufacturers in the production of its Nexus devices, and it released multiple hardware products in October 2016, including the Google Pixel smartphone, Google Home smart speaker, Google Wifi mesh wireless router, and Google Daydream virtual reality headset. Google has also experimented with becoming an Internet carrier. In February 2010, it announced Google Fiber, a fiber-optic infrastructure that was installed in Kansas City; in April 2015, it launched Project Fi in the United States, combining Wi-Fi and cellular networks from different providers; and in 2016, it announced the Google Station initiative to make public Wi-Fi available around the world, with initial deployment in India.[6]
Alexa Internet monitors commercial web traffic and lists Google.com as the most visited website in the world. Several other Google services also figure in the top 100 most visited websites, including YouTube and Blogger. Google is the most valuable brand in the world as of 2017,[7] but has received significant criticism involving issues such as privacy concerns, tax avoidance, antitrust, censorship, and search neutrality. Google's mission statement is "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful", and its unofficial slogan was "Don't be evil". In October 2015, the motto was replaced in the Alphabet corporate code of conduct by the phrase "Do the right thing", while the original one was retained in the code of conduct of Google.[8]Around May 2018, the slogan was silently removed from the code's clauses, leaving only one generic reference in its last paragraph.[9]
Contents
History
Main article: History of Google
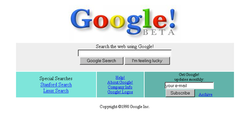
Google's original homepage had a simple design because the company founders had little experience in HTML, the markup language used for designing web pages.[10]
Google began in January 1996 as a research project by Larry Page and Sergey Brin when they were both PhD students at Stanford University in Stanford, California.[11]
While conventional search engines ranked results by counting how many times the search terms appeared on the page, the two theorized about a better system that analyzed the relationships among websites.[12] They called this new technology PageRank; it determined a website's relevance by the number of pages, and the importance of those pages that linked back to the original site.[13][14]
Page and Brin originally nicknamed their new search engine "BackRub", because the system checked backlinks to estimate the importance of a site.[15][16][17] Eventually, they changed the name to Google; the name of the search engine originated from a misspelling of the word "googol",[18][19] the number 1 followed by 100 zeros, which was picked to signify that the search engine was intended to provide large quantities of information.[20] Originally, Google ran under Stanford University's website, with the domains google.stanford.edu[21] and z.stanford.edu.[22]
The domain name for Google was registered on September 15, 1997,[23] and the company was incorporated on September 4, 1998. It was based in the garage of a friend (Susan Wojcicki[11]) in Menlo Park, California. Craig Silverstein, a fellow PhD student at Stanford, was hired as the first employee.[11][24][25]
Financing (1998) and initial public offering (2004)
Google was initially funded by an August 1998 contribution of $100,000 from Andy Bechtolsheim, co-founder of Sun Microsystems; the money was given before Google was incorporated.[27] Google received money from three other angel investors in 1998: Amazon.com founder Jeff Bezos, Stanford University computer science professor David Cheriton, and entrepreneur Ram Shriram.[28]
After some additional, small investments through the end of 1998 to early 1999,[28] a new $25 million round of funding was announced on June 7, 1999,[29] with major investors including the venture capital firms Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers and Sequoia Capital.[27]
Early in 1999, Brin and Page decided they wanted to sell Google to Excite. They went to Excite CEO George Bell and offered to sell it to him for $1 million. He rejected the offer. Vinod Khosla, one of Excite's venture capitalists, talked the duo down to $750,000, but Bell still rejected it.[30]
Google's initial public offering (IPO) took place five years later, on August 19, 2004. At that time Larry Page, Sergey Brin, and Eric Schmidt agreed to work together at Google for 20 years, until the year 2024.[31]
At IPO, the company offered 19,605,052 shares at a price of $85 per share.[32][33] Shares were sold in an online auction format using a system built by Morgan Stanley and Credit Suisse, underwriters for the deal.[34][35] The sale of $1.67 bn (billion) gave Google a market capitalization of more than $23bn.[36] By January 2014, its market capitalization had grown to $397bn.[37] The vast majority of the 271 million shares remained under the control of Google, and many Google employees became instant paper millionaires. Yahoo!, a competitor of Google, also benefitted because it owned 8.4 million shares of Google before the IPO took place.[38]
There were concerns that Google's IPO would lead to changes in company culture. Reasons ranged from shareholder pressure for employee benefit reductions to the fact that many company executives would become instant paper millionaires.[39] As a reply to this concern, co-founders Brin and Page promised in a report to potential investors that the IPO would not change the company's culture.[40] In 2005, articles in The New York Times[41] and other sources began suggesting that Google had lost its anti-corporate, no evil philosophy.[42][43][44] In an effort to maintain the company's unique culture, Google designated a Chief Culture Officer, who also serves as the Director of Human Resources. The purpose of the Chief Culture Officer is to develop and maintain the culture and work on ways to keep true to the core values that the company was founded on: a flat organization with a collaborative environment.[45] Google has also faced allegations of sexism and ageism from former employees.[46][47] In 2013, a class action against several Silicon Valley companies, including Google, was filed for alleged "no cold call" agreements which restrained the recruitment of high-tech employees.[48]
The stock performed well after the IPO, with shares hitting $350 for the first time on October 31, 2007,[49] primarily because of strong sales and earnings in the online advertising market.[50] The surge in stock price was fueled mainly by individual investors, as opposed to large institutional investors and mutual funds.[50] GOOG shares split into GOOG class C shares and GOOGL class A shares.[51] The company is listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange under the ticker symbols GOOGL and GOOG, and on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol GGQ1. These ticker symbols now refer to Alphabet Inc., Google's holding company, since the fourth quarter of 2015.[52]
Growth
In March 1999, the company moved its offices to Palo Alto, California,[53] which is home to several prominent Silicon Valley technology start-ups.[54] The next year, Google began selling advertisements associated with search keywords against Page and Brin's initial opposition toward an advertising-funded search engine.[55][11] To maintain an uncluttered page design, advertisements were solely text-based.[56]
This model of selling keyword advertising was first pioneered by Goto.com, an Idealab spin-off created by Bill Gross.[57][58] When the company changed names to Overture Services, it sued Google over alleged infringements of the company's pay-per-click and bidding patents. Overture Services would later be bought by Yahoo! and renamed Yahoo! Search Marketing. The case was then settled out of court; Google agreed to issue shares of common stock to Yahoo! in exchange for a perpetual license.[59]
In 2001, Google received a patent for its PageRank mechanism.[60] The patent was officially assigned to Stanford University and lists Lawrence Page as the inventor. In 2003, after outgrowing two other locations, the company leased an office complex from Silicon Graphics, at 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway in Mountain View, California.[61] The complex became known as the Googleplex, a play on the word googolplex, the number one followed by a googol zeroes. The Googleplex interiors were designed by Clive Wilkinson Architects. Three years later, Google bought the property from SGI for $319 million.[62] By that time, the name "Google" had found its way into everyday language, causing the verb "google" to be added to the Merriam-Webster Collegiate Dictionary and the Oxford English Dictionary, denoted as: "to use the Google search engine to obtain information on the Internet".[63][64] The first use of "Google" as a verb in pop culture happened on the TV series Buffy the Vampire Slayer, in 2002.[65]
In 2005, The Washington Post reported on a 700 percent increase in third-quarter profit for Google, largely thanks to large companies shifting their advertising strategies from newspapers, magazines, and television to the Internet.[66] In January 2008, all the data that passed through Google's MapReduce software component had an aggregated size of 20 petabytes per day.[67][68][69] In 2009, a CNN report about top political searches of 2009 noted that "more than a billion searches" are being typed into Google on a daily basis.[70] In May 2011, the number of monthly unique visitors to Google surpassed one billion for the first time, an 8.4 percent increase from May 2010 (931 million).[71]
The year 2012 was the first time that Google generated $50 billion in annual revenue, generating $38 billion the previous year. In January 2013, then-CEO Larry Page commented, "We ended 2012 with a strong quarter ... Revenues were up 36% year-on-year, and 8% quarter-on-quarter. And we hit $50 billion in revenues for the first time last year – not a bad achievement in just a decade and a half."[72]
2013 onward
Google announced the launch of a new company, called Calico, on September 19, 2013, to be led by Apple, Inc. chairman Arthur Levinson. In the official public statement, Page explained that the "health and well-being" company would focus on "the challenge of ageing and associated diseases".[73]
Google celebrated its 15-year anniversary on September 27, 2013, and in 2016 it celebrated its 18th birthday with an animated Doodle shown on web browsers around the world.[74] although it has used other dates for its official birthday.[75] The reason for the choice of September 27 remains unclear, and a dispute with rival search engine Yahoo! Search in 2005 has been suggested as the cause.[76][77]
The Alliance for Affordable Internet (A4AI) was launched in October 2013; Google is part of the coalition of public and private organizations that also includes Facebook, Intel, and Microsoft. Led by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the A4AI seeks to make Internet access more affordable so that access is broadened in the developing world, where only 31% of people are online. Google will help to decrease Internet access prices so they fall below the UN Broadband Commission's worldwide target of 5% of monthly income.[78]
The corporation's consolidated revenue for the third quarter of 2013 was reported in mid-October 2013 as $14.89 billion, a 12 percent increase compared to the previous quarter.[79] Google's Internet business was responsible for $10.8 billion of this total, with an increase in the number of users' clicks on advertisements.[80]
According to Interbrand's annual Best Global Brands report, Google has been the second most valuable brand in the world (behind Apple Inc.) in 2013,[81] 2014,[82] 2015,[83] and 2016, with a valuation of $133 billion.[84]
In September 2015, Google engineering manager Rachel Potvin revealed details about Google's software code at an engineering conference. She revealed that the entire Google codebase, which spans every single service it develops, consists of over 2 billion lines of code. All that code is stored in a code repository available to all 25,000 Google engineers, and the code is regularly copied and updated on 10 Google data centers. To keep control, Potvin said Google has built its own "version control system", called "Piper", and that "when you start a new project, you have a wealth of libraries already available to you. Almost everything has already been done." Engineers can make a single code change and deploy it on all services at the same time. The only major exceptions are that the PageRank search results algorithm is stored separately with only specific employee access, and the code for the Android operating system and the Google Chrome browser are also stored separately, as they don't run on the Internet. The "Piper" system spans 85 TB of data. Google engineers make 25,000 changes to the code each day and on a weekly basis change approximately 15 million lines of code across 250,000 files. With that much code, automated bots have to help. Potvin reported, "You need to make a concerted effort to maintain code health. And this is not just humans maintaining code health, but robots too.” Bots aren't writing code, but generating a lot of the data and configuration files needed to run the company's software. "Not only is the size of the repository increasing," Potvin explained, "but the rate of change is also increasing. This is an exponential curve."[85][86]
As of October 2016, Google operates 70 offices in more than 40 countries.[87] Alexa, a company that monitors commercial web traffic, lists Google.com as the most visited website in the world.[88] Several other Google services also figure in the top 100 most visited websites, including YouTube[89] and Blogger.[90]
Acquisitions and partnerships
Main article: List of mergers and acquisitions by Alphabet
2000–2009
In 2001, Google acquired Deja News, the operators of a large archive of materials from Usenet.[91][92] Google rebranded the archive as Google Groups, and by the end of the year, it had expanded the history back to 1981.[93][94]
In April 2003, Google acquired Applied Semantics, a company specializing in making software applications for the online advertising space.[95][96] The AdSense contextual advertising technology developed by Applied Semantics was adopted into Google's advertising efforts.[97][94]
In 2004, Google acquired Keyhole, Inc.[98] Keyhole's eponymous product was later renamed Google Earth.
In April 2005, Google acquired Urchin Software, using their Urchin on Demand product (along with ideas from Adaptive Path's Measure Map) to create Google Analytics in 2006.
In October 2006, Google announced that it had acquired the video-sharing site YouTube for $1.65 billion in Google stock,[99][100] and the deal was finalized on November 13, 2006.[101][102]
On April 13, 2007, Google reached an agreement to acquire DoubleClick for $3.1 billion, transferring to Google valuable relationships that DoubleClick had with Web publishers and advertising agencies.[103] The deal was approved despite anti-trust concerns raised by competitors Microsoft and AT&T.[104]
In addition to the many companies Google has purchased, the firm has partnered with other organizations for research, advertising, and other activities. In 2005, Google partnered with NASA Ames Research Center to build 1,000,000 square feet (93,000 m2) of offices.[105]
In 2005 Google partnered with AOL[106] to enhance each other's video search services. In 2006 Google and Fox Interactive Media of News Corporation entered into a $900 million agreement to provide search and advertising on the then-popular social networking site MySpace.[107]
In 2007, Google began sponsoring NORAD Tracks Santa, displacing the former sponsor AOL. NORAD Tracks Santa purports to follow Santa Claus' progress on Christmas Eve,[108] using Google Earth to "track Santa" in 3-D for the first time.[109][110]
In 2008, Google developed a partnership with GeoEye to launch a satellite providing Google with high-resolution (0.41 m monochrome, 1.65 m color) imagery for Google Earth. The satellite was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on September 6, 2008.[111] Google also announced in 2008 that it was hosting an archive of Life Magazine's photographs.[112][113]
2010–present
In 2010, Google Energy made its first investment in a renewable energy project, putting $38.8 million into two wind farms in North Dakota. The company announced the two locations will generate 169.5 megawatts of power, enough to supply 55,000 homes. The farms, which were developed by NextEra Energy Resources, will reduce fossil fuel use in the region and return profits. NextEra Energy Resources sold Google a twenty-percent stake in the project to get funding for its development.[114] In February 2010, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission FERC granted Google an authorization to buy and sell energy at market rates.[115] The order specifically states that Google Energy—a subsidiary of Google—holds the rights "for the sale of energy, capacity, and ancillary services at market-based rates", but acknowledges that neither Google Energy nor its affiliates "own or control any generation or transmission" facilities.[116] The corporation exercised this authorization in September 2013 when it announced it would purchase all the electricity produced by the not-yet-built 240-megawatt Happy Hereford wind farm.[117]
Also in 2010, Google purchased Global IP Solutions, a Norway-based company that provides web-based teleconferencing and other related services. This acquisition enabled Google to add telephone-style services to its list of products.[118] On May 27, 2010, Google announced it had also closed the acquisition of the mobile ad network AdMob. This occurred days after the Federal Trade Commission closed its investigation into the purchase.[119] Google acquired the company for an undisclosed amount.[120] In July 2010, Google signed an agreement with an Iowa wind farm to buy 114 megawatts of energy for 20 years.[121]
On April 4, 2011, The Globe and Mail reported that Google bid $900 million for 6000 Nortel Networks patents.[122]
On August 15, 2011, Google made its largest-ever acquisition to-date when it announced that it would acquire Motorola Mobility for $12.5 billion[123][124] subject to approval from regulators in the United States and Europe. In a post on Google's blog, Google Chief Executive and co-founder Larry Page revealed that the acquisition was a strategic move to strengthen Google's patent portfolio. The company's Android operating system has come under fire in an industry-wide patent battle, as Apple and Microsoft have sued Android device makers such as HTC, Samsung, and Motorola.[125] The merger was completed on May 22, 2012, after the approval of China.[126]
This purchase was made in part to help Google gain Motorola's considerable patent portfolio on mobile phones and wireless technologies, to help protect Google in its ongoing patent disputes with other companies,[127] mainly Apple and Microsoft,[125] and to allow it to continue to freely offer Android.[128] After the acquisition closed, Google began to restructure the Motorola business to fit Google's strategy. On August 13, 2012, Google announced plans to lay off 4000 Motorola Mobility employees.[129] On December 10, 2012, Google sold the manufacturing operations of Motorola Mobility to Flextronics for $75 million.[130] As a part of the agreement, Flextronics will manufacture undisclosed Android and other mobile devices.[131] On December 19, 2012, Google sold the Motorola Home business division of Motorola Mobility to Arris Group for $2.35 billion in a cash-and-stock transaction. As a part of this deal, Google acquired a 15.7% stake in Arris Group valued at $300 million.[132][133]
In June 2013, Google acquired Waze, a $966 million deal.[134] While Waze would remain an independent entity, its social features, such as its crowdsourced location platform, were reportedly valuable integrations between Waze and Google Maps, Google's own mapping service.[135]
On January 26, 2014, Google announced it had agreed to acquire DeepMind Technologies, a privately held artificial intelligence company from London. DeepMind describes itself as having the ability to combine the best techniques from machine learning and systems neuroscience to build general-purpose learning algorithms. DeepMind's first commercial applications were used in simulations, e-commerce and games. As of December 2013, it was reported that DeepMind had roughly 75 employees.[136] Technology news website Recode reported that the company was purchased for $400 million though it was not disclosed where the information came from. A Google spokesman would not comment of the price.[137][138] The purchase of DeepMind aids in Google's recent growth in the artificial intelligence and robotics community.[139]
On January 29, 2014, Google announced that it would divest Motorola Mobility to Lenovo for $2.91 billion, a fraction of the original $12.5 billion price paid by Google to acquire the company. Google retained all but 2000 of Motorola's patents and entered into cross-licensing deals.[140]
On September 21, 2017, HTC announced a "cooperation agreement" in which it would sell non-exclusive rights to certain intellectual property, as well as smartphone talent, to Google for $1.1 billion.[141][142][143]
On December 6, 2017, Google made its first investment in India and picked up a significant minority stake in hyper-local concierge and delivery player Dunzo.[144] The Benguluru-based startup received $12 million investment in Google's series B funding round.[145]
On March 29, 2018, Google led a Series C funding round into online-to-offline fashion e-commerce start-up Fynd.[146] It was its second direct investment in India with an undisclosed amount.[147][148] In this way, Google is also looking to build an ecosystem in India across high-frequency hyper-local transactions as well as in the healthcare, financial services, and education sectors.
On August 23, 2018, Google deleted 39 YouTube accounts, 13 Google+ accounts and 6 blogs on Blogger due to their engagement in politically motivated phishing, the deleted accounts were found to be tied with Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting (IRIB).[149][150][151]
Google data centers
See also: Google data centers
Google data centers are located in North and South America, Asia, Europe.[152]
Traditionally, Google relied on parallel computing on commodity hardware[153] like mainstream x86 computers similar to home PCs[154] to keep costs per query low.[155] In 2005, it started developing its own designs, which were only revealed in 2009.[155]
In October 2013, The Washington Post reported that the U.S. National Security Agency intercepted communications between Google's data centers, as part of a program named MUSCULAR.[156][157] This wiretapping was made possible because Google did not encrypt data passed inside its own network.[158] Google began encrypting data sent between data centers in 2013.[159]
Google's most efficient data center runs at 35 °C (95 °F) using only fresh air cooling, requiring no electrically powered air conditioning; the servers run so hot that humans cannot go near them for extended periods.[160]
An August 2011 report estimated that Google had about 900,000 servers in their data centers, based on energy usage. The report does state that "Google never says how many servers are running in its data centers."[161]
In December 2016, Google announced that—starting in 2017—it will power all of its data centers, as well as all of its offices, from 100% renewable energy. The commitment will make Google "the world's largest corporate buyer of renewable power, with commitments reaching 2.6 gigawatts (2,600 megawatts) of wind and solar energy". Google also stated that it does not count that as its final goal; it says that "since the wind doesn't blow 24 hours a day, we'll also broaden our purchases to a variety of energy sources that can enable renewable power, every hour of every day". Additionally, the project will "help support communities" around the world, as the purchase commitments will "result in infrastructure investments of more than $3.5 billion globally", and will "generate tens of millions of dollars per year in revenue to local property owners, and tens of millions more to local and national governments in tax revenue".[162][163][164]
Alphabet
Main article: Alphabet Inc.
On August 10, 2015, Google announced plans to reorganize its various interests as a conglomerate called Alphabet. Google became Alphabet's leading subsidiary, and will continue to be the umbrella company for Alphabet's Internet interests. Upon completion of the restructure, Sundar Pichai became CEO of Google, replacing Larry Page, who became CEO of Alphabet.[165][166][167]
On September 1, 2017, Google Inc. announced its plans of restructuring as a limited liability company, Google LLC, as a wholly owned subsidiary of XXVI Holdings Inc., which is formed as a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. to hold the equity of its other subsidiaries, including Google LLC and other bets.[168]
Products and services
See also: List of Google products
Advertising
For the 2006 fiscal year, the company reported $10.492 billion in total advertising revenues and only $112 million in licensing and other revenues.[169] In 2011, 96% of Google's revenue was derived from its advertising programs.[170] In addition to its own algorithms for understanding search requests, Google uses technology from the company DoubleClick, to project user interest and target advertising to the search context and the user history.[171][172]
In 2007, Google launched "AdSense for Mobile", taking advantage of the emerging mobile advertising market.[173]
Google Analytics allows website owners to track where and how people use their website, for example by examining click rates for all the links on a page.[174] Google advertisements can be placed on third-party websites in a two-part program. Google's AdWords allows advertisers to display their advertisements in the Google content network, through a cost-per-click scheme.[175] The sister service, Google AdSense, allows website owners to display these advertisements on their website and earn money every time ads are clicked.[176]
One of the criticisms of this program is the possibility of click fraud, which occurs when a person or automated script clicks on advertisements without being interested in the product, causing the advertiser to pay money to Google unduly. Industry reports in 2006 claimed that approximately 14 to 20 percent of clicks were fraudulent or invalid.[177]
In February 2003, Google stopped showing the advertisements of Oceana, a non-profit organization protesting a major cruise ship's sewage treatment practices. Google cited its editorial policy at the time, stating "Google does not accept advertising if the ad or site advocates against other individuals, groups, or organizations."[178] In June 2008, Google reached an advertising agreement with Yahoo!, which would have allowed Yahoo! to feature Google advertisements on its web pages. The alliance between the two companies was never completely realized because of antitrust concerns by the U.S. Department of Justice. As a result, Google pulled out of the deal in November 2008.[179][180]
In July 2016, Google started rejecting all flash-based adverts replacing them by HTML5. Google’s plan was to go “100% HTML5” beginning on January 2, 2017.[181]
Search engine
Main articles: Google Search and Google Images
According to comScore market research from November 2009, Google Search is the dominant search engine in the United States market, with a market share of 65.6%.[182] Google indexes billions of web pages to allow users to search for the information they desire through the use of keywords and operators.[183]
In 2003, The New York Times complained about Google's indexing, claiming that Google's caching of content on its site infringed its copyright for the content.[184] In both Field v. Google and Parker v. Google, the United States District Court of Nevada ruled in favor of Google.[185][186] The publication 2600: The Hacker Quarterly has compiled a list of words that google's new instant search feature will not search.[187]
Google Watch has criticized Google's PageRank algorithms, saying that they discriminate against new websites and favor established sites.[188]
Google also hosts Google Books. The company began scanning books and uploading limited previews, and full books were allowed, into its new book search engine. The Authors Guild, a group that represents 8,000 U.S. authors, filed a class action suit in a New York City federal court against Google in 2005 over this service. Google replied that it is in compliance with all existing and historical applications of copyright laws regarding books.[189] Google eventually reached a revised settlement in 2009 to limit its scans to books from the U.S., the UK, Australia, and Canada.[190] Furthermore, the Paris Civil Court ruled against Google in late 2009, asking it to remove the works of La Martinière (Éditions du Seuil) from its database.[191] In competition with Amazon.com, Google sells digital versions of new books.[192]
On July 21, 2010, in response to Bing, Google updated its image search to display a streaming sequence of thumbnails that enlarge when pointed at. Although web searches still appear in a batch per page format, on July 23, 2010, dictionary definitions for certain English words began appearing above the linked results for web searches.[193]
The "Hummingbird" update to the Google search engine was announced in September 2013. The update was introduced over the month prior to the announcement and allows users ask the search engine a question in natural language rather than entering keywords into the search box.[194]
In August 2016, Google announced two major changes to its mobile search results. The first change removes the "mobile-friendly" label that highlighted easy to read pages from its mobile search results page. For the second change, the company—starting on January 10, 2017—will punish mobile pages that show intrusive interstitial advertisements when a user first opens a page. Such pages will also rank lower in Google search results.[195]
In May 2017, Google enabled a new "Personal" tab in Google Search, letting users search for content in their Google accounts' various services, including email messages from Gmail and photos from Google Photos.[196][197]
Enterprise services
Main article: G Suite
G Suite is a monthly subscription offering for organizations and businesses to get access to a collection of Google's services, including Gmail, Google Drive and Docs, Sheets, and Slides, with additional administrative tools, unique domain names, and 24/7 support.[198]
Google Search Appliance was launched in February 2002, targeted toward providing search technology for larger organizations.[11] Google launched the Mini three years later, which was targeted at smaller organizations. Late in 2006, Google began to sell Custom Search Business Edition, providing customers with an advertising-free window into Google.com's index. The service was renamed Google Site Search in 2008.[199] Site Search customers were notified by email in late March 2017 that no new licenses for Site Search would be sold after April 1, 2017, but that customer and technical support would be provided for the duration of existing license agreements.[200][201]
On March 15, 2016, Google announced the introduction of Google Analytics 360 Suite, "a set of integrated data and marketing analytics products, designed specifically for the needs of enterprise-class marketers" which can be integrated with BigQuery on the Google Cloud Platform. Among other things, the suite is designed to help "enterprise class marketers" "see the complete customer journey", generate "useful insights", and "deliver engaging experiences to the right people".[202] Jack Marshall of The Wall Street Journal wrote that the suite competes with existing marketing cloud offerings by companies including Adobe, Oracle, Salesforce, and IBM.[203]
Business incubator
On September 24, 2012,[204] Google launched Google for Entrepreneurs, a largely not-for-profit business incubator providing startups with co-working spaces known as Campuses, with assistance to startup founders that may include workshops, conferences, and mentorships.[205] Presently, there are 7 Campus locations in Berlin, London, Madrid, Seoul, São Paulo, Tel Aviv, and Warsaw.
Consumer services
Web-based services
Google offers Gmail, and the newer variant Inbox,[206] for email,[207] Google Calendar for time-management and scheduling,[208] Google Maps for mapping, navigation and satellite imagery,[209] Google Drive for cloud storage of files,[210] Google Docs, Sheets and Slides for productivity,[210] Google Photos for photo storage and sharing,[211] Google Keep for note-taking,[212] Google Translate for language translation,[213] YouTube for video viewing and sharing,[214] and Google+, Allo, and Duo for social interaction.[215][216][217]
In April 2018, Google introduced the curated job feature for Indian users to search jobs more efficiently. The feature is built in coordination with major job search platforms like Aasaanjobs, Freshersworld, Headhonchos, IBM Talent Management Solutions, LinkedIn and many more.[218]
In May 2018, Google launched a new app named Neighbourly in India through which users can explore information about local places and also know about the people living nearby.[219]
In August 2018, Google introduced Navlekha (a Sanskrit word meaning, “a new way to write.”) initiative, which will help Indian authors to publish their content in regional languages.[220]
On 7 September, 2018, Google launched a mobile app for Android named ‘Blog Compass’ to help bloggers track the visitors and explore through the most relevant and trending topics to write.[221][222]
Software
Google develops the Android mobile operating system,[223] as well as its smartwatch,[224] television,[225] car,[226] and Internet of things-enabled smart devices variations.[227]
It also develops the Google Chrome web browser,[228] and Chrome OS, an operating system based on Chrome.[229]
Hardware
In January 2010, Google released Nexus One, the first Android phone under its own, "Nexus", brand.[230] It spawned a number of phones and tablets under the "Nexus" branding[231] until its eventual discontinuation in 2016, replaced by a new brand called, Pixel.[232]
In 2011, the Chromebook was introduced, described as a "new kind of computer" running Chrome OS.[233]
In July 2013, Google introduced the Chromecast dongle, that allows users to stream content from their smartphones to televisions.[234][235]
In June 2014, Google announced Google Cardboard, a simple cardboard viewer that lets user place their smartphone in a special front compartment to view virtual reality (VR) media.[236][237]
In April 2016, Recode reported that Google had hired Rick Osterloh, Motorola Mobility's former President, to head Google's new hardware division.[238] In October 2016, Osterloh stated that "a lot of the innovation that we want to do now ends up requiring controlling the end-to-end user experience",[232] and Google announced several hardware platforms:
- The Pixel and Pixel XL smartphones with the Google Assistant, a next-generation contextual voice assistant, built-in.[239]
- Google Home, an Amazon Echo-like voice assistant placed in the house that can answer voice queries, play music, find information from apps (calendar, weather etc.), and control third-party smart home appliances (users can tell it to turn on the lights, for example).[240]
- Daydream View virtual reality headset that lets Android users with compatible Daydream-ready smartphones put their phones in the headset and enjoy VR content.[241]
- Google Wifi, a connected set of Wi-Fi routers to simplify and extend coverage of home Wi-Fi.[242]
Google will release its 'Google Pixel Watch' in the fall of 2018.[243]
Internet services
In February 2010, Google announced the Google Fiber project, with experimental plans to build an ultra-high-speed broadband network for 50,000 to 500,000 customers in one or more American cities.[244][245] Following Google's corporate restructure to make Alphabet Inc. its parent company, Google Fiber was moved to Alphabet's Access division.[246][247]
In April 2015, Google announced Project Fi, a mobile virtual network operator, that combines Wi-Fi and cellular networks from different telecommunication providers in an effort to enable seamless connectivity and fast Internet signal.[248][249][250]
In September 2016, Google began its Google Station initiative, a project for public Wi-Fi at railway stations in India. Caesar Sengupta, VP for Google's next billion users, told The Verge that 15,000 people get online for the first time thanks to Google Station and that 3.5 million people use the service every month. The expansion meant that Google was looking for partners around the world to further develop the initiative, which promised "high-quality, secure, easily accessible Wi-Fi".[251] By December, Google Station had been deployed at 100 railway stations,[252] and in February, Google announced its intention to expand beyond railway stations, with a plan to bring citywide Wi-Fi to Pune.[253][254]
Other products
Google launched its Google News service in 2002, an automated service which summarizes news articles from various websites.[255] In March 2005, Agence France Presse (AFP) sued Google for copyright infringement in federal court in the District of Columbia, a case which Google settled for an undisclosed amount in a pact that included a license of the full text of AFP articles for use on Google News.[256]
In May 2011, Google announced Google Wallet, a mobile application for wireless payments.[257]
In 2013, Google launched Google Shopping Express, a delivery service initially available only in San Francisco and Silicon Valley.[258]
Google Alerts is a content change detection and notification service, offered by the search engine company Google. The service sends emails to the user when it finds new results—such as web pages, newspaper articles, or blogs—that match the user's search term.[259][260][261]
In July 2015 Google released DeepDream, an image recognition software capable of creating psychedelic images using a convolutional neural network.[262][263][264]
Google introduced its Family Link service in March 2017, letting parents buy Android Nougat-based Android devices for kids under 13 years of age and create a Google account through the app, with the parents controlling the apps installed, monitor the time spent using the device, and setting a "Bedtime" feature that remotely locks the device.[265][266][267]
In April 2017, Google launched AutoDraw, a web-based tool using artificial intelligence and machine learning to recognize users' drawings and replace scribbles with related stock images that have been created by professional artists.[268][269][270] The tool is built using the same technology as QuickDraw, an experimental game from Google's Creative Lab where users were tasked with drawing objects that algorithms would recognize within 20 seconds.[271]
In May 2017, Google added "Family Groups" to several of its services. The feature, which lets users create a group consisting of their family members' individual Google accounts, lets users add their "Family Group" as a collaborator to shared albums in Google Photos, shared notes in Google Keep, and common events in Google Calendar. At announcement, the feature is limited to Australia, Brazil, Canada, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, Russia, Spain, United Kingdom and United States.[272][273]
APIs
Google APIs are a set of application programming interfaces (APIs) developed by Google which allow communication with Google Services and their integration to other services. Examples of these include Search, Gmail, Translate or Google Maps. Third-party apps can use these APIs to take advantage of or extend the functionality of the existing services.
Other websites
Google Developers is Google's site for software development tools, APIs, and technical resources. The site contains documentation on using Google developer tools and APIs—including discussion groups and blogs for developers using Google's developer products.
Google Labs was a page created by Google to demonstrate and test new projects.
Google owns the top-level domain 1e100.net which is used for some servers within Google's network. The name is a reference to the scientific E notation representation for 1 googol, 1E100 = 1 × 10100.[274]
In March 2017, Google launched a new website, opensource.google.com, to publish its internal documentation for Google Open Source projects.[275][276]
In June 2017, Google launched "We Wear Culture", a searchable archive of 3,000 years of global fashion. The archive, a result of collaboration between Google and over 180 museums, schools, fashion institutes, and other organizations, also offers curated exhibits of specific fashion topics and their impact on society.[277][278]
Corporate affairs and culture

Then-CEO, now Chairman of Google Eric Schmidt with cofounders Sergey Brin and Larry Page (left to right) in 2008.
On Fortune magazine's list of the best companies to work for, Google ranked first in 2007, 2008 and 2012[279][280][281] and fourth in 2009 and 2010.[282][283] Google was also nominated in 2010 to be the world's most attractive employer to graduating students in the Universum Communications talent attraction index.[284] Google's corporate philosophy includes principles such as "you can make money without doing evil," "you can be serious without a suit," and "work should be challenging and the challenge should be fun."[285]
Employees
As of March 2018, Google has 85,050 employees.[4] Google's 2017 diversity report states that 31 percent of its workforce are women and 69 percent are men, with the ethnicity of its workforce being predominantly white (56%) and Asian (35%).[286] Within tech roles, however, 20 percent were women; and 25 percent of leadership roles were held by women.[286] The report also announced that Intel's former vice-president, CDO, and CHRO Danielle Brown would be joining Google as its new Vice-President of Diversity.[286] A March 2013 report was presented at EclipseCon2013 which detailed that Google had over 10,000 developers based in more than 40 offices.[287][needs update]
Google's employees are hired based on a hierarchical system. Employees are split into six hierarchies based on experience and can range "from entry-level data center workers at level one to managers and experienced engineers at level six."[288]
After the company's IPO in 2004, founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page and CEO Eric Schmidt requested that their base salary be cut to $1. Subsequent offers by the company to increase their salaries were turned down, primarily because their main compensation continues to come from owning stock in Google. Before 2004, Schmidt made $250,000 per year, and Page and Brin each received an annual salary of $150,000.[289]
In March 2008, Sheryl Sandberg, then vice-president of global online sales and operations, began her position as chief operating officer of Facebook.[290][291] In 2009, early employee Tim Armstrong left to become CEO of AOL. In July 2012, Google's first female engineer, Marissa Mayer, left Google to become Yahoo!'s CEO.[292]

New employees are called "Nooglers," and are given a propeller beanie cap to wear on their first Friday.[294]
As a motivation technique, Google uses a policy often called Innovation Time Off, where Google engineers are encouraged to spend 20% of their work time on projects that interest them. Some of Google's services, such as Gmail, Google News, Orkut, and AdSense originated from these independent endeavors.[295] In a talk at Stanford University, Marissa Mayer, Google's Vice-President of Search Products and User Experience until July 2012, showed that half of all new product launches in the second half of 2005 had originated from the Innovation Time Off.[296]
Office locations and headquarters
Mountain View
Main article: Googleplex
Google's headquarters in Mountain View, California is referred to as "the Googleplex", a play on words on the number googolplex and the headquarters itself being a complex of buildings. The lobby is decorated with a piano, lava lamps, old server clusters, and a projection of search queries on the wall. The hallways are full of exercise balls and bicycles. Many employees have access to the corporate recreation center. Recreational amenities are scattered throughout the campus and include a workout room with weights and rowing machines, locker rooms, washers and dryers, a massage room, assorted video games, table football, a baby grand piano, a billiard table, and ping pong. In addition to the recreation room, there are snack rooms stocked with various foods and drinks, with special emphasis placed on nutrition.[297] Free food is available to employees 24/7, with the offerings provided by paid vending machines prorated based on and favoring those of better nutritional value.[298]
Google's extensive amenities are not available to all of its workers. Temporary workers such as book scanners do not have access to shuttles, Google cafes, or other perks.[299]
New York City
In 2006, Google moved into about 300,000 square feet (27,900 m2) of office space in New York City, at 111 Eighth Avenue in Manhattan. The office was designed and built specially for Google, and houses its largest advertising sales team, which has been instrumental in securing large partnerships.[300] The New York headquarters includes a game room, micro-kitchens, and a video game area.[301] In 2010, Google bought the building housing the headquarter, in a deal that valued the property at around $1.9 billion, the biggest for a single building in the United States that year.[302][303] In February 2012, Google moved additional employees to the New York City campus, with a total of around 2,750 employees.[304] In 2018, Google's parent company Alphabet bought Chelsea Market building for $2.4 billion nearby its current New York HQ. The sale is touted as one of the Most Expensive Real estate Transactions for a single building in history of New York.[305][306][307][308]
Other U.S. cities
By late 2006, Google established a new headquarters for its AdWords division in Ann Arbor, Michigan.[309] In November 2006, Google opened offices on Carnegie Mellon's campus in Pittsburgh, focusing on shopping-related advertisement coding and smartphone applications and programs.[310][311] Other office locations in the U.S. include Atlanta, Georgia; Austin, Texas; Boulder, Colorado; Cambridge, Massachusetts; San Francisco, California; Seattle, Washington; Reston, Virginia, and Washington, D.C.[312]
In October 2006, the company announced plans to install thousands of solar panels to provide up to 1.6 megawatts of electricity, enough to satisfy approximately 30% of the campus' energy needs.[313] The system will be the largest solar power system constructed on a U.S. corporate campus and one of the largest on any corporate site in the world.[313] In addition, Google announced in 2009 that it was deploying herds of goats to keep grassland around the Googleplex short, helping to prevent the threat from seasonal bush fires while also reducing the carbon footprint of mowing the extensive grounds.[314][315] The idea of trimming lawns using goats originated from Bob Widlar, an engineer who worked for National Semiconductor.[316] In 2008, Google faced accusations in Harper's Magazine of being an "energy glutton". The company was accused of employing its "Don't be evil" motto and its public energy-saving campaigns to cover up or make up for the massive amounts of energy its servers require.[317]
International locations
Internationally, Google has over 78 offices in more than 50 countries.[318] It also has product research and development operations in cities around the world, namely Sydney (birthplace location of Google Maps)[319] and London (part of Android development).[320]
In November 2013, Google announced plans for a new London headquarter, a notable 1 million square foot office able to accommodate 4,500 employees. Recognized as one of the biggest ever commercial property acquisitions at the time of the deal's announcement in January,[321] Google submitted plans for the new headquarter to the Camden Council in June 2017. The new building, if approved, will feature a rooftop garden with a running track, giant moving blinds, a swimming pool, and a multi-use games area for sports.[322][323]
In May 2015, Google announced its intention to create its own campus in Hyderabad, India. The new campus, reported to be the company's largest outside the United States, will accommodate 13,000 employees.[324][325]
Doodles
Main article: Google Doodle
Since 1998, Google has been designing special, temporary alternate logos to place on their homepage intended to celebrate holidays, events, achievements and people. The first Google Doodle was in honor of the Burning Man Festival of 1998.[326][327] The doodle was designed by Larry Page and Sergey Brin to notify users of their absence in case the servers crashed. Subsequent Google Doodles were designed by an outside contractor, until Larry and Sergey asked then-intern Dennis Hwang to design a logo for Bastille Day in 2000. From that point onward, Doodles have been organized and created by a team of employees termed "Doodlers".[328]
Easter eggs and April Fools' Day jokes
Main articles: List of Google April Fools' Day jokes and List of Google Easter eggs
Google has a tradition of creating April Fools' Day jokes. On April 1, 2000, Google MentalPlex allegedly featured the use of mental power to search the web.[329] In 2007, Google announced a free Internet service called TiSP, or Toilet Internet Service Provider, where one obtained a connection by flushing one end of a fiber-optic cable down their toilet.[330]Also in 2007, Google's Gmail page displayed an announcement for Gmail Paper, allowing users to have email messages printed and shipped to them.[331] In 2008, Google announced Gmail Custom time where users could change the time that the email was sent.[332]
In 2010, Google changed its company name to Topeka in honor of Topeka, Kansas, whose mayor changed the city's name to Google for a short amount of time in an attempt to sway Google's decision in its new Google Fiber Project.[333][334] In 2011, Google announced Gmail Motion, an interactive way of controlling Gmail and the computer with body movements via the user's webcam.[335]
Google's services contain easter eggs, such as the Swedish Chef's "Bork bork bork," Pig Latin, "Hacker" or leetspeak, Elmer Fudd, Pirate, and Klingon as language selections for its search engine.[336] The search engine calculator provides the Answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything from Douglas Adams' The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy.[337] When searching the word "recursion", the spell-checker's result for the properly spelled word is exactly the same word, creating a recursive link.[338]
When searching for the word "anagram," meaning a rearrangement of letters from one word to form other valid words, Google's suggestion feature displays "Did you mean: nag a ram?"[339] In Google Maps, searching for directions between places separated by large bodies of water, such as Los Angeles and Tokyo, results in instructions to "kayak across the Pacific Ocean." During FIFA World Cup 2010, search queries including "World Cup" and "FIFA" caused the "Goooo...gle" page indicator at the bottom of every result page to read "Goooo...al!" instead.[340]
Philanthropy
Main article: Google.org
In 2004, Google formed the not-for-profit philanthropic Google.org, with a start-up fund of $1 billion.[341] The mission of the organization is to create awareness about climate change, global public health, and global poverty. One of its first projects was to develop a viable plug-in hybrid electric vehicle that can attain 100 miles per gallon. Google hired Larry Brilliant as the program's executive director in 2004[342] and Megan Smith has since replaced him has director.[343]
In 2008, Google announced its "project 10100" which accepted ideas for how to help the community and then allowed Google users to vote on their favorites.[344] After two years of silence, during which many wondered what had happened to the program,[345] Google revealed the winners of the project, giving a total of ten million dollars to various ideas ranging from non-profit organizations that promote education to a website that intends to make all legal documents public and online.[346]
In March 2007, in partnership with the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute (MSRI), Google hosted the first Julia Robinson Mathematics Festival at its headquarters in Mountain View.[347] In 2011, Google donated 1 million euros to International Mathematical Olympiad to support the next five annual International Mathematical Olympiads (2011–2015).[348][349] In July 2012, Google launched a "Legalize Love" campaign in support of gay rights.[350]
Tax avoidance
Further information: Corporation tax in the Republic of Ireland § Multinational tax schemes
Google uses various tax avoidance strategies. Out of the five largest American technology companies, it pays the lowest taxes to the countries of origin of its revenues. Google between 2007 and 2010 saved $3.1 billion in taxes by shuttling non-U.S. profits through Ireland and the Netherlands and then to Bermuda. Such techniques lower its non-U.S. tax rate to 2.3 per cent, while normally the corporate tax rate in for instance the UK is 28 per cent.[351] This has reportedly sparked a French investigation into Google's transfer pricing practices.[352]
Following criticism of the amount of corporate taxes that Google paid in the United Kingdom, Chairman Eric Schmidt said, "It's called capitalism. We are proudly capitalistic." During the same December 2012 interview, Schmidt confirmed that the company had no intention of paying more to the UK exchequer.[353]
Google Vice-President Matt Brittin testified to the Public Accounts Committee of the UK House of Commons that his UK sales team made no sales and hence owed no sales taxes to the UK.[354] In January 2016, Google reached a settlement with the UK to pay £130m in back taxes plus higher taxes in future.[355]
Environment
Since 2007, Google has aimed for carbon neutrality in regard to its operations.[356]
Google disclosed in September 2011 that it "continuously uses enough electricity to power 200,000 homes", almost 260 million watts or about a quarter of the output of a nuclear power plant. Total carbon emissions for 2010 were just under 1.5 million metric tons, mostly due to fossil fuels that provide electricity for the data centers. Google said that 25 percent of its energy was supplied by renewable fuels in 2010. An average search uses only 0.3 watt-hours of electricity, so all global searches are only 12.5 million watts or 5% of the total electricity consumption by Google.[357]
In 2007, Google launched a project centered on developing renewable energy, titled the "Renewable Energy Cheaper than Coal (RE<C)" project.[358] However, the project was canceled in 2014, after engineers Ross Koningstein and David Fork understood, after years of study, that "best-case scenario, which was based on our most optimistic forecasts for renewable energy, would still result in severe climate change", writing that they "came to the conclusion that even if Google and others had led the way toward a wholesale adoption of renewable energy, that switch would not have resulted in significant reductions in carbon dioxide emissions".[359]
In June 2013, The Washington Post reported that Google had donated $50,000 to the Competitive Enterprise Institute, a libertarian think tank that calls human carbon emissions a positive factor in the environment and argues that global warming is not a concern.[360]
In July 2013, it was reported that Google had hosted a fundraising event for Oklahoma Senator Jim Inhofe, who has called climate change a "hoax".[361] In 2014 Google cut ties with the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) after pressure from the Sierra Club, major unions and Google's own scientists because of ALEC's stance on climate change and opposition to renewable energy.[362]
In November 2017, Google bought 536 megawatts of wind power. The purchase made the firm reach 100% renewable energy. The wind energy comes from two power plants in South Dakota, one in Iowa and one in Oklahoma.[363]
Lobbying
In 2013, Google ranked 5th in lobbying spending, up from 213th in 2003. In 2012, the company ranked 2nd in campaign donations of technology and Internet sections.[364]
Litigation
Main article: Google litigation
Google has been involved in a number of lawsuits including the High-Tech Employee Antitrust Litigation which resulted in Google being one of four companies to pay a $415 million settlement to employees.[365]
On June 27, 2017, the company received a record fine of €2.42 billion from the European Union for "promoting its own shopping comparison service at the top of search results."[366] Commenting on the penalty, New Scientist magazine said: "The hefty sum – the largest ever doled out by the EU's competition regulators – will sting in the short term, but Google can handle it. Alphabet, Google’s parent company, made a profit of $2.5 billion (€2.2 billion) in the first six weeks of 2017 alone. The real impact of the ruling is that Google must stop using its dominance as a search engine to give itself the edge in another market: online price comparisons." The company disputed the ruling.[367]
Criticism and controversy
Main articles: Criticism of Google and Censorship by Google
Google's market dominance has led to prominent media coverage, including criticism of the company over issues such as aggressive tax avoidance,[368] search neutrality, copyright, censorship of search results and content,[369] and privacy.[370][371] Other criticisms include alleged misuse and manipulation of search results, its use of others' intellectual property, concerns that its compilation of data may violate people's privacy, and the energy consumption of its servers, as well as concerns over traditional business issues such as monopoly, restraint of trade, anti-competitive practices, and patent infringement.
Google adhered to the Internet censorship policies of China,[372] enforced by means of filters colloquially known as "The Great Firewall of China". The Intercept reported in August 2018 that Google is developing for the people's Republic of China a censored version of its search engine (known as Dragonfly) "that will blacklist websites and search terms about human rights, democracy, religion, and peaceful protest".[373][374]
Google's mission statement, from the outset, was "to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful",[375] and its unofficial slogan is "Don't be evil".[376] In October 2015, a related motto was adopted in the Alphabet corporate code of conduct by the phrase: "Do the right thing".[377] The original motto was retained in the code of conduct of Google, now a subsidiary of Alphabet.[8]
Google's commitment to such robust idealism has been increasingly called into doubt due to a number of the firm's actions and behaviors which appear to contradict this.[378][379]
Following media reports about PRISM, NSA's massive electronic surveillance program, in June 2013, several technology companies were identified as participants, including Google.[380] According to leaks of said program, Google joined the PRISM program in 2009.[381]
On August 8, 2017, Google fired employee James Damore after he distributed a memo throughout the company which argued that "Google's ideological echo chamber" and bias clouded their thinking about diversity and inclusion, and that it is also biological factors, not discrimination alone, that cause the average woman to be less interested than men in technical positions.[382] Google CEO Sundar Pichai accused Damore in violating company policy by "advancing harmful gender stereotypes in our workplace", and he was fired on the same day.[383][384][385] New York Times columnist David Brooks argued Pichai had mishandled the case, and called for his resignation.[386][387]
Reportedly, Google's influenced New America think tank to expel their Open Markets research group, after the group has criticized Google monopolistic power and supported the EU $2.7B fine of Google.[388][389]
Google was working with the United States Department of Defense on drone software called "Project Maven" that could be used to improve the accuracy of drone strikes.[390]Thousands of Google employees, including senior engineers, have signed a letter urging Google CEO Sundar Pichai to end a controversial contract with the Pentagon.[391]
Legal controversies
In 2017, David Elliot and Chris Gillespie argued before the Ninth Circuit of the United States Court of Appeals that "google" had suffered genericide. The controversy began in 2012 when Gillespie acquired 763 domain names containing the word "google." Google promptly filed a complaint with the National Arbitration Forum (NAF). Elliot then filed a petition for canceling the Google trademark. Ultimately, the court ruled in favor of Google because Elliot failed to show a preponderance of evidence showing the genericide of "google."[392]
See also
- AngularJS
- Comparison of web search engines
- Don't Be Evil
- Google (verb)
- Google Balloon Internet
- Google Catalogs
- Google China
- Google bomb
- Google Chrome Experiments
- Google Get Your Business Online
- Google logo
- Google Maps
- Google platform
- Google Street View
- Google tax
- Google Ventures – venture capital fund
- Google X
- Life sciences division of Google X
- Googlebot – web crawler
- Googlization
- List of Google apps for Android
- List of mergers and acquisitions by Alphabet
- Apple, Inc.
- Outline of Google
- Reunion
- Ungoogleable
- Surveillance capitalism
- Calico
JavaScript Example
Waiting...
4 Years Diploma in Engineering under BTEB. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quam
Scanning...
Scanning...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quam
Waiting...
Waiting...
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quam
Computer Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamComputer Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamComputer Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamElectrical Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamElectrical Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamElectrical Tread Course
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Praesent eget risus vitae massa semper aliquam quis mattis quamNOTICE
DPBT.p NOTICE admission:Diploma-in-Engineering course admission starts at all Government/equivalent polytechnic institution under Bangladesh Technical Education Board (BTEB). The last date of application is 12 June 2013. Students who passed SSC in 2011, 2012 & 2013 with GPA 3.00 in Mathematics/Higher Mathematics and have total GPA 3.50 are eligible to apply. And students who passed 2 year Trade Course approved by BTEB are also eligible to apply. For more information about the admission pleaseADMISSION FEE
Admission Fee
| # | Description | Fee |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Admission Fee | 5000 BDT |
| 2 | Admission Form | 200 BDT |
| 3 | ID Card | 200 BDT |
| 4 | Registration Fee | 600 BDT |
| Total : | 6000 BDT |
TUITION FEE (Diploma)
-
Electrical
- Semester Fee: 8 X 6000 = 48000
- Tuition Fess: 48 X 1000 = 48000
- Total: 96000 BDT GET IT NOW
-
Civil
- Semester Fee: 8 X 6000 = 48000
- Tuition Fess: 48 X 1000 = 48000
- Total: 96000 BDT GET IT NOW
-
Computer
- Semester Fee: 8 X 6000 = 48000
- Tuition Fess: 48 X 1000 = 48000
- Total: 96000 BDT GET IT NOW
-
Electrical
- Semester Fee: 8 X 6000 = 48000
- Tuition Fess: 48 X 1000 = 48000
- Total: 96000 BDT GET IT NOW
TUITION FEE (Tread Course)
Tread Course Program Information
| # | Course name | Duration(Month) | Admission Fee | Course Fess | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IT Support Service | 1 | 200 TK | 2800 TK | 3000 TK |
| 2 | IT Spport Service | 3 | 200 TK | 3800 TK | 4000 TK |
| 3 | Graphics Design | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 4 | Web Design | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 5 | Outsourcing | 1 | 200 TK | 2800 TK | 3000 TK |
| 6 | Electrical House waring | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 7 | Electrical House waring | 6 | 200 TK | 7800 TK | 8000 TK |
| 8 | Electrical Machine Maintenance | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 9 | Electrical Machine Maintenance | 6 | 200 TK | 7800 TK | 8000 TK |
| 10 | Motor/fan Re-waring | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 11 | RAC | 6 | 200 TK | 7800 TK | 8000 TK |
| 12 | Dress Making & Trailering | 3 | 200 TK | 2800 TK | 3000 TK |
| 13 | Dress Making & Trailering | 6 | 200 TK | 4800 TK | 5000 TK |
| 14 | Swing Machine Operation | 3 | 200 TK | 3800 TK | 4000 TK |
| 15 | Driving With Auto.. | 6 | 200 TK | 9800 TK | 10000 TK |
| 16 | Driving | 2 | 200 TK | 9800 TK | 10000 TK |
| 17 | Engine Mechanic | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 18 | Motor Cycle Mechanic | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 19 | Electronics Works | 6 | 200 TK | 7800 TK | 8000 TK |
| 20 | Consumer Electronics | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 21 | Television Servising | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
| 22 | Mobile Phone Servicing | 3 | 200 TK | 5800 TK | 6000 TK |
free web
Click the button to display a random number.
Admin & CEO
Md.TowfiqHossain
Web Design and Development
!!Always With You!! | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
~~``May Allah bless You`~~!!!May Allah Bless You!!! | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
t
|
infoshareplus.help
Registration Form
Use tab keys to move from one input field to the next.Click the button to display what day it is today.

free web
Click the button to display a random number.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Labels
Update new fast
Labels:
Update new fast
Location:
Aah towfiq Road, Bangladesh
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps






















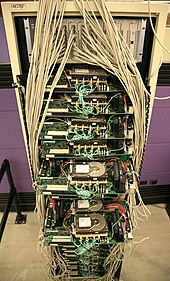






















Comments